Emre Demir

I hold a Master's Degree in Computer Science from the Technical University of Munich. My master's thesis, completed in collaboration with the German Aerospace Center (DLR), focused on optimizing neural network designs for enhanced hardware compatibility. I possess a Bachelor's Degree in Computer Engineering.
Currently, I am employed as a Machine Learning Engineer at Certivity, where I specialize in addressing regulatory challenges through the application of Natural Language Processing (NLP) and advanced software solutions.
Portfolio
AutoML, Computer Vision
Earth Observation Neural Architecture Search Benchmark
Neural Architecture Search(NAS): Neural Architecture Search (NAS) automates the process of architecture design of neural networks. NAS approaches optimize the topology of the networks, incl. how to connect nodes and which operators to choose. User-defined optimization metrics can thereby include accuracy, model size or inference time to arrive at an optimal architecture for specific applications.
In this work, I have worked in a team of 5 and I was responsible for the design and creation of the whole model training pipeline on High Performance Computer. In the end we were able to train more than thousand deep learning models with just a single submission.

Federated Learning
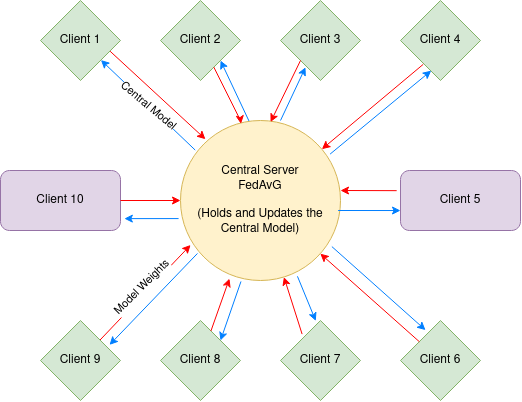
Federated Learning on Diabetes Data on non-iid setting
Federated Learning on Diabetes Data:The project utilizes a logistic regression model on 10 distinct clients to explore the concept of federated learning. By leveraging the Flower framework, the simulation is executed on a local machine, enabling efficient implementation and evaluation of federated learning techniques. Each client in the project possesses a unique dataset, characterized by varying sizes of imbalanced data points. Further details on the dataset distribution can be found in the “dirichlet_dist.py” file. The dataset comprises 2 classes and 21 features, with each client containing an identical number of features. The project adopts the Federated Averaging strategy as a key mechanism for aggregating the client models. Through this approach, the project aims to examine the effectiveness and potential benefits of federated learning in a logistic regression setting.
Computer Vision
3D Deformable Object Registration using Neural Networks
3D Point Correspondence: The 3D point correspondence problem is a fundamental problem in computer vision that involves matching points in two or more images of a 3D scene. The goal is to find the corresponding points between the images, which can be used to reconstruct the 3D structure of the scene. This problem arises in a wide range of applications, such as object tracking, stereo vision, and structure from motion.
In this work, we have used different methods to find point correspondences for 3D untextured and deformable objects with 2D images. Best solution was using SurfEmbeddings deep Learning model. You can find the related code in github repository and use it for your own.
Also, we have tried out if adding artificial textures to untextured objects increases the performance and it reduced the convergence time of the model significantly.

NLP
Picky-Rabbit
Picky Rabbit: Picky Rabbit is an OpenAI LLM-powered chatbot that provides information about the contents of packaged food products. It helps users make informed choices by offering details on ingredients, nutritional values, allergens, and more. In the second version, the chatbot incorporates Similarity Search with LLMs, enabling it to respond by considering the food data stored in the compact vector database FAISS.

Just for Fun
Etymology CLI in Rust
tret_cli: It is a simple CLI tool that wrote while learning Rust language. After enterıng a word, it returns the etymological root of that word togeter with the meaning.

